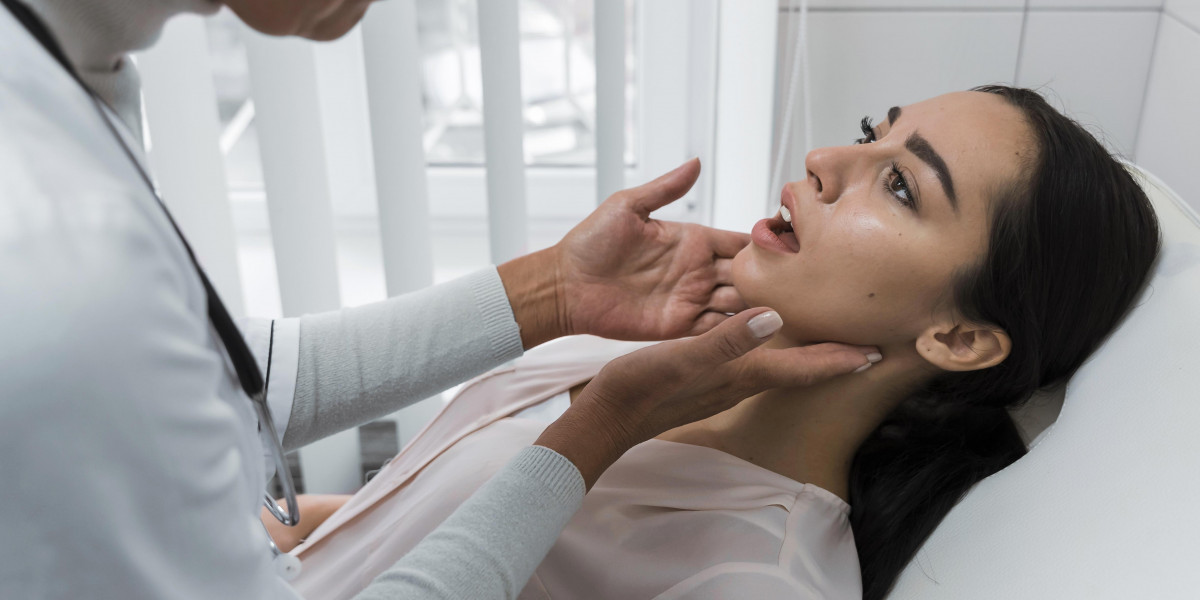
If left untreated, thyroid disease can cause serious complications that affect various body systems and significantly reduce overall quality of life. The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, heart function, and hormone balance, so any disruption can lead to widespread health problems over time. Delayed diagnosis or lack of proper treatment may allow symptoms to worsen, increasing the risk of long-term damage to the heart, bones, mental health, and reproductive system. In more advanced cases, medical management alone may not be sufficient, and consultation with a specialist, such as a thyroid surgeon West Yorkshire may be necessary to assess treatment options and prevent further complications. Understanding these risks highlights the importance of early detection, regular monitoring, and timely medical intervention to maintain overall health and well-being.
Complications of Untreated Thyroid Disease
Cardiovascular issues
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can cause heart problems. Hypothyroidism can cause elevated cholesterol levels, which increases the risk of heart disease and atherosclerosis. Meanwhile, hyperthyroidism can cause high blood pressure, a fast or irregular heartbeat, and even heart failure if not properly treated.
Mental health conditions
Thyroid imbalances can have a profound impact on mental health. Hypothyroidism is often associated with depression, mood swings, and slow cognitive function, while hyperthyroidism can cause anxiety, restlessness, and irritability. Long-term, untreated thyroid issues can worsen these conditions, making daily activities difficult.
Myxedema (severe hypothyroidism)
Myxedema is a rare but fatal condition caused by extremely low levels of thyroid hormones. Symptoms include extreme fatigue, hypothermia, confusion, and in severe cases, coma. Myxedema requires immediate medical intervention because it can be fatal if left untreated.
Osteoporosis. Untreated hyperthyroidism can cause a decrease in bone density because excess thyroid hormones affect the body's calcium balance. Over time, the risk of fractures and osteoporosis increases, especially in women and the elderly.
Infertility and pregnancy complications
Thyroid disease can affect fertility by causing irregular menstrual cycles and ovulation. In pregnant women, untreated thyroid disease can cause complications such as miscarriage, preterm birth, low birth weight, and developmental delays. Maintaining thyroid health before and during pregnancy is important for the health of both mother and baby.
Goiter and compression symptoms
Persistent hypothyroidism or iodine deficiency can cause enlargement of the thyroid gland (goiter). Large goiters can cause pressure on the neck, resulting in difficulty swallowing, breathing problems, and a hoarse voice.
Peripheral neuropathy
In cases of long-term untreated hypothyroidism, peripheral nerves can become damaged, causing numbness, tingling, or pain, especially in the hands and feet.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Thyroid hormones play a role in liver metabolism, and both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can increase the risk of NAFLD. This condition, which involves the accumulation of fat in the liver, can cause inflammation and, in severe cases, liver disease.
Cognitive decline and memory issues
Severe hypothyroidism can affect brain function, causing memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and slowed thought processes. These issues can worsen over time, especially in older adults, if thyroid disease is not treated early.
Coma and death
In severe cases of untreated thyroid disease, particularly severe hypothyroidism (myxedema) and hyperthyroidism (thyroid storm), complications can lead to coma or death. Immediate medical intervention is critical in these situations. Early detection and treatment of thyroid disease is important to prevent potentially life-threatening complications. With proper care, regular monitoring, and lifestyle changes, people with thyroid disease can avoid its serious effects and maintain a better quality of life.
Causes of Thyroid Disease
Thyroid disease can have various causes, depending on the type of disease affecting the thyroid gland. Here are some of the main factors that cause thyroid disease:
Thyroid inflammation
Conditions that cause inflammation of the thyroid, such as thyroiditis, can affect the proper functioning of the gland and cause thyroid disease.
Thyroid nodules
The presence of tumors or nodules in the thyroid gland can disrupt normal hormone production, potentially causing hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. Autoimmune disorders, such as Graves' disease and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. In autoimmune thyroid conditions, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland. Graves' disease causes overproduction of hormones (hyperthyroidism), while Hashimoto's thyroiditis often results in an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism).
Exposure to excessive radioactive iodine
Large amounts of radioactive iodine, whether from the environment or certain medical procedures, can damage thyroid cells and affect hormone production.
Side effects of radiation therapy to the neck
Radiation treatments aimed at the neck region for other medical conditions can unintentionally affect the thyroid, causing thyroid disease.
Hormonal changes from pregnancy
Hormonal changes during and after pregnancy can trigger thyroid issues, such as postpartum thyroiditis, which can cause hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Congenital thyroid problems
Some people are born with thyroid abnormalities, which can cause lifelong thyroid problems if not treated promptly.
Genetic predisposition
Family history is an important risk factor for thyroid disease. If thyroid disease runs in the family, the individual is more likely to develop the same condition.
Smoking
Smoking can interfere with thyroid function, especially because tobacco contains substances that can impair iodine absorption and increase the risk of autoimmune thyroid disorders.
Iodine deficiency
Because iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production, insufficient iodine consumption can cause conditions such as goiter and hypothyroidism.
Frequent exposure to stress
Chronic stress can cause hormone imbalances and trigger or worsen thyroid problems, especially in people who are predisposed to thyroid disease. These factors often interact in complex ways, causing different types of thyroid disease. Knowing these causes can help in early detection and proactive management of thyroid health.
Thyroid Disease Prevention
To maintain thyroid gland health and reduce the risk of developing thyroid disease, consider the following lifestyle habits:
Eat a balanced diet
Eating a regular diet of nutritious foods at the right times supports the health of various parts of the body, including the thyroid gland. Foods rich in iodine, such as seaweed and fish, are particularly beneficial because iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production.
Avoid excessive exercise
While regular exercise is beneficial, excessive exercise can affect the uptake of thyroid hormones into the body's cells. This can cause hormonal imbalances, and a person may experience stubborn fat around the waist even when physically active.
Quit smoking
Smoking contains harmful chemicals that affect iodine absorption and increase inflammation in the thyroid gland. Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of thyroid issues and improve overall health.
Limit unnecessary exposure to X-rays
Frequent exposure to X-rays, especially to the neck, can damage thyroid cells due to the presence of radioactive elements. Avoid X-rays unless necessary to protect thyroid health.
Take your medication as prescribed
Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions for proper dosage and use. Overuse of some medications, such as lithium, can harm your thyroid function, so it's important to take them correctly.
Manage stress effectively
Avoid stressors as much as possible, as chronic stress can affect thyroid health. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, and moderate exercise can help maintain hormone balance and support thyroid function. Through these activities, you can maintain thyroid health and reduce the risk of developing thyroid disease. Regular checkups with a health specialist can also help in the early detection and management of any thyroid-related issues.
Conclusion
Thyroid disease can have a significant impact on overall health if it is not diagnosed and treated on time. Understanding its causes, complications, and prevention strategies helps people take early action and make informed health decisions. Regular check-ups, healthy lifestyle habits, and proper medical treatment play a vital role in managing thyroid conditions effectively. When symptoms involve the neck, voice, or swallowing, or when advanced care is needed, consulting the Best ENT surgeon can help ensure accurate evaluation and appropriate treatment. With timely medical support and ongoing care, individuals with thyroid disease can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.