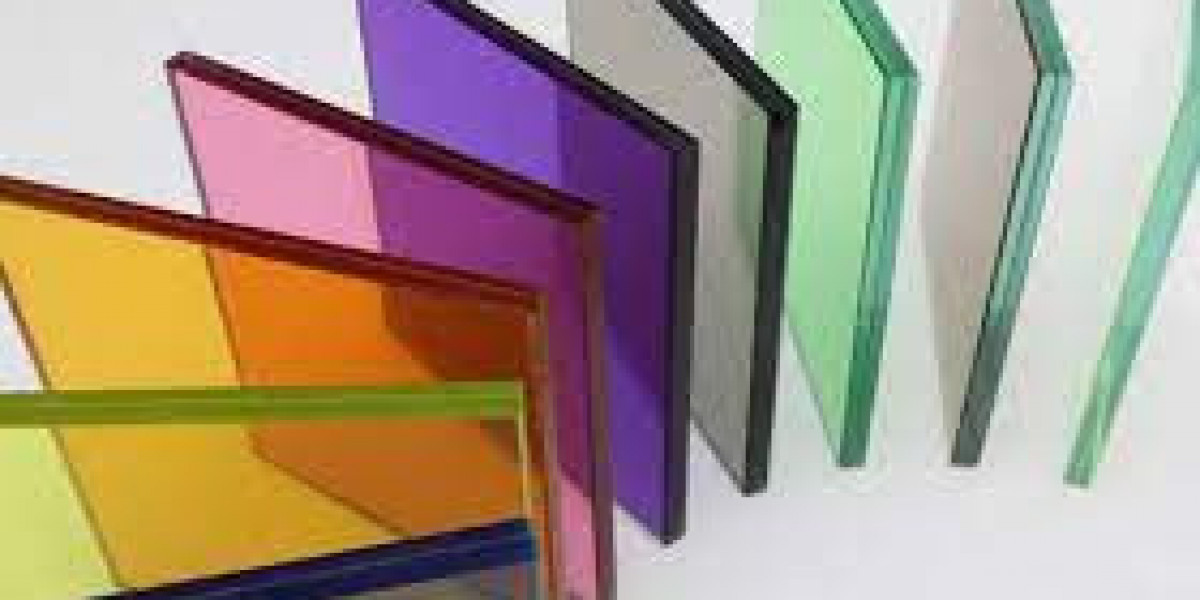
Filter glass plays a vital role in controlling light transmission across optical systems. From cameras and sensors to laboratory instruments, it ensures that only specific wavelengths pass through, improving performance and accuracy. But despite its importance, issues with filter glass can create serious challenges in imaging, medical, and industrial applications. To explore reliable solutions, you can check filter glass options designed for advanced optical use.
Why Filter Glass Matters in Optics
High-quality filter glass enhances image clarity, reduces unwanted light, and ensures accurate measurement in spectroscopy and optical devices. However, when defects or wear occur, it directly impacts system reliability, leading to inaccurate results or costly downtime.
Common Problems with Filter Glass
1. Surface Damage and Scratches
Even minor scratches affect light transmission and scatter, degrading the quality of captured images or measurements. In sensitive equipment, this can make data unreliable.
2. Wavelength Shifts
Filter glass designed for specific wavelengths may shift due to heat, humidity, or aging. This leads to poor signal isolation in devices such as microscopes or fluorescence instruments.
3. Coating Defects
Filters often rely on thin-film coatings to enhance performance. When coatings peel, crack, or degrade, optical efficiency declines sharply.
4. Durability Under Harsh Environments
In aerospace, defense, or industrial applications, filter glass is exposed to extreme temperatures and pressure. Without proper material strength, glass may fracture or lose optical accuracy.
Industries Affected by Filter Glass Failures
Medical Imaging: Poor filter performance can compromise diagnosis in X-ray and fluorescence equipment.
Industrial Inspection: Defective filters reduce accuracy in laser and machine vision systems.
Consumer Electronics: Cameras and sensors with faulty glass face lower image quality.
Research & Defense: High-precision optics require durable and stable filter glass for reliability.
How to Overcome These Issues
Manufacturers are addressing these problems with advanced solutions:
Scratch-resistant coatings for longer durability.
Heat-stable materials to minimize wavelength shifts.
Improved multilayer coatings for sharper optical performance.
Quality testing standards to detect defects before deployment.
To ensure consistent results, businesses often choose specialized filter glass designed for specific industries like medical, aerospace, or scientific research.
Conclusion
Filter glass remains essential for precision optics, but challenges such as surface damage, coating defects, and wavelength instability create risks across industries. Addressing these problems with high-quality materials and advanced coatings ensures durability, accuracy, and efficiency in optical systems. For organizations relying on imaging, sensing, or laser technology, proactive investment in reliable filter glass is the key to long-term performance.