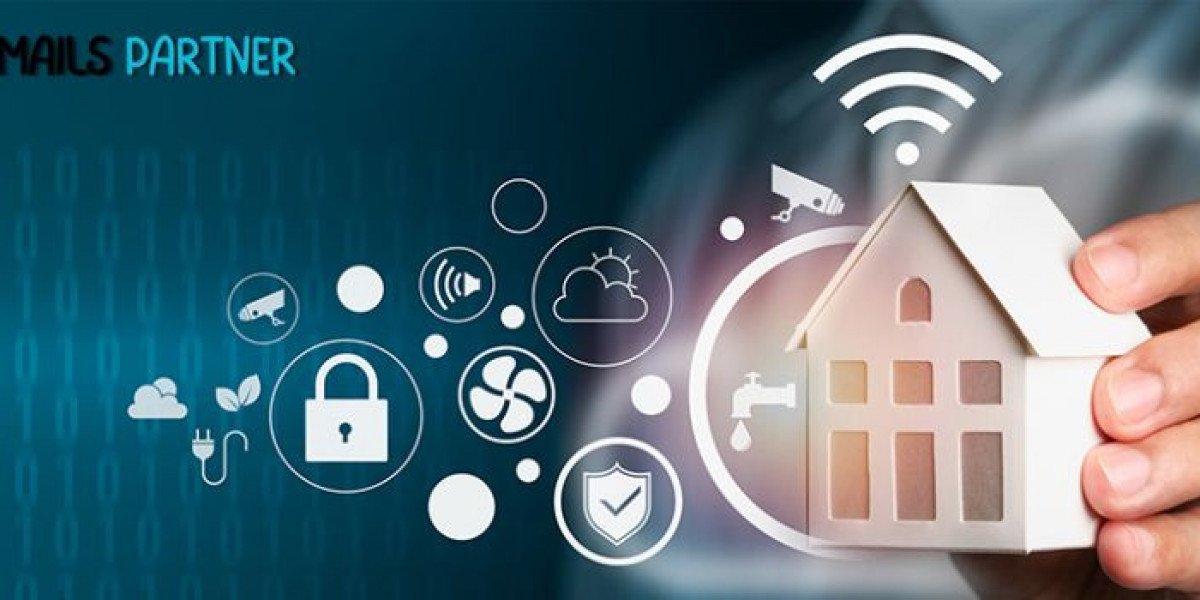
The World of Smart Homes and IoT Devices is rapidly transforming how we live, interact, and manage our daily activities. In a few short years, the concept of connected homes has evolved from a futuristic dream to an accessible reality for millions of households worldwide. Smart lights, thermostats, security cameras, and voice assistants are no longer luxuries—they’re essential components of the modern home ecosystem. Powered by the Internet of Things (IoT), these devices communicate seamlessly, bringing automation, convenience, and energy efficiency to everyday life. As technology continues to advance, smart homes are reshaping our lifestyles, redefining comfort, and raising important questions about privacy, security, and sustainability.
1. Understanding the World of Smart Homes and IoT Devices
At its core, a smart home is a residence equipped with interconnected devices that can be remotely monitored, controlled, and automated. The Internet of Things (IoT) is the underlying technology that enables these devices to connect through the internet and share data in real time. From smart refrigerators that remind you to buy milk to thermostats that adjust temperature based on your habits, IoT devices create a responsive environment that adapts to human needs.
IoT devices typically use sensors, wireless networks, and cloud computing to function. These components collect and process data, allowing devices to make intelligent decisions. For example, a smart lighting system can detect occupancy in a room and adjust brightness automatically. Similarly, a smart lock can recognize your smartphone and unlock the door without requiring a key. Together, these innovations make homes more efficient, personalized, and secure.
2. The Evolution of Smart Homes
The journey toward smart homes began decades ago with simple automation systems such as garage door openers and programmable thermostats. However, the real transformation started in the early 2000s with the widespread availability of Wi-Fi and mobile devices. The integration of voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri accelerated the adoption of smart technology by making it more user-friendly and affordable.
Today, nearly every household appliance—from washing machines to vacuum cleaners—can be integrated into a connected ecosystem. According to industry reports, the global smart home market is projected to surpass $200 billion by 2030, driven by advancements in AI, 5G connectivity, and energy-efficient innovations. The future points toward homes that not only respond to human commands but also predict needs before we even express them.
3. Key Components of Smart Homes
The World of Smart Homes and IoT Devices comprises several key components, each designed to enhance convenience, security, and sustainability. Let’s explore the main categories:
a. Smart Lighting Systems
Smart lighting allows users to control brightness, color, and scheduling through mobile apps or voice commands. Motion sensors can automatically turn lights on or off, saving energy and improving safety. Philips Hue and LIFX are popular examples of smart lighting systems.
b. Smart Thermostats
Devices like Google Nest and Ecobee learn user habits and automatically adjust temperatures for maximum comfort and energy efficiency. These thermostats can even detect when you’re away from home and lower energy consumption accordingly.
c. Smart Security Systems
From doorbell cameras to smart locks and motion detectors, IoT-powered security systems provide real-time monitoring and alerts. They enable remote access, allowing homeowners to check live video feeds or lock doors from anywhere in the world.
d. Smart Appliances
Smart refrigerators, ovens, and washing machines can communicate with users via smartphone apps. They provide updates on maintenance needs, suggest recipes based on ingredients, and optimize energy use during off-peak hours.
e. Smart Entertainment Systems
IoT has revolutionized entertainment through devices like smart TVs, wireless speakers, and streaming hubs that integrate seamlessly. With voice control and AI-driven recommendations, these systems personalize content experiences.
f. Smart Health and Fitness Devices
Wearables such as smartwatches and health monitors connect to home networks, tracking physical activity, sleep, and even air quality. Some systems can integrate with smart home assistants to offer health insights and reminders.
4. Benefits of Smart Homes and IoT Devices
The appeal of smart homes lies in the multitude of benefits they offer. Here are the most significant advantages:
a. Convenience and Automation
The greatest strength of IoT devices is automation. With voice commands or scheduled routines, homeowners can control lighting, temperature, and appliances without manual effort. This convenience simplifies daily life and enhances productivity.
b. Enhanced Security
Smart cameras, motion detectors, and video doorbells provide round-the-clock surveillance. Real-time alerts and remote access make it easier to monitor properties, deter burglars, and respond quickly to security threats.
c. Energy Efficiency
IoT devices help reduce energy consumption by optimizing usage patterns. Smart thermostats and lighting systems adjust based on occupancy, while connected appliances operate more efficiently, reducing electricity bills and environmental impact.
d. Cost Savings
While the initial investment in smart devices can be high, long-term savings from reduced energy use and maintenance costs often outweigh the upfront expenses. Many homeowners experience significant reductions in utility bills.
e. Accessibility
Smart homes are particularly beneficial for elderly individuals or people with disabilities. Voice commands, automation, and remote controls enhance accessibility, promoting independence and comfort.
f. Customization
IoT systems allow users to tailor their environments. Whether it’s adjusting the lighting mood, automating morning routines, or personalizing temperature settings, smart homes adapt to individual preferences seamlessly.
5. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Smart Homes
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a central role in shaping the World of Smart Homes and IoT Devices. It allows devices to move beyond simple automation to intelligent prediction. AI algorithms analyze data collected from sensors and user behavior to anticipate needs and offer personalized experiences.
For example, an AI-powered thermostat learns your daily schedule and adjusts the temperature automatically before you arrive home. Similarly, smart refrigerators can suggest grocery lists based on past consumption patterns. The more data these systems collect, the smarter and more intuitive they become.
In the near future, AI assistants may act as digital home managers, controlling multiple devices simultaneously and optimizing energy usage, comfort, and safety based on real-time data analysis.
6. Challenges in the World of Smart Homes and IoT Devices
While the benefits are impressive, smart homes come with their own set of challenges that must be addressed for the technology to achieve its full potential.
a. Privacy Concerns
IoT devices constantly collect data about user habits, preferences, and even conversations. This data, if mishandled, can pose significant privacy risks. Many users remain skeptical about who has access to their information and how it’s used.
b. Cybersecurity Threats
The interconnected nature of IoT makes smart homes vulnerable to hacking. A single compromised device can grant access to the entire network. Manufacturers and users must implement robust security measures, such as strong passwords, firewalls, and regular updates.
c. Compatibility Issues
With numerous brands and technologies available, ensuring compatibility among devices can be challenging. While initiatives like Matter (a universal smart home standard) aim to solve this issue, interoperability remains a major concern.
d. High Initial Costs
Although prices are falling, setting up a fully functional smart home can still be expensive. Devices, installation, and maintenance can add up, making it less accessible for average consumers.
e. Data Overload
As IoT devices generate massive amounts of data, managing and analyzing this information efficiently becomes difficult. Cloud storage solutions and AI-driven analytics are helping, but the problem continues to grow with expanding networks.
7. Sustainability and Smart Homes
One of the most promising aspects of smart homes is their potential to support sustainability. Smart devices are designed to minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and promote eco-friendly habits. Smart irrigation systems conserve water by adjusting schedules based on weather data, while smart meters monitor energy use and encourage homeowners to adopt greener lifestyles.
Moreover, integrating renewable energy sources like solar panels with smart home systems enhances sustainability. Homeowners can monitor energy production, consumption, and storage through intuitive dashboards, optimizing their carbon footprint.
8. The Future of Smart Homes and IoT Devices
The next decade promises revolutionary advancements in the World of Smart Homes and IoT Devices. Several emerging trends will shape the future:
a. Voice and Gesture Control
The future will see more natural interactions between humans and devices through voice and gesture recognition, making home control even more intuitive.
b. 5G Connectivity
5G technology will provide faster, more reliable connections, enabling seamless communication among a greater number of IoT devices.
c. Predictive Maintenance
IoT-enabled appliances will predict breakdowns before they occur, scheduling maintenance automatically to prevent costly repairs.
d. Smart Cities Integration
Smart homes will connect with larger smart city infrastructures, contributing to efficient energy grids, waste management, and transportation systems.
e. Enhanced Data Security
Advancements in blockchain and encryption will enhance privacy, allowing secure, transparent data sharing among devices.
f. Emotional AI and Personalized Living
Future systems may use emotional AI to interpret user moods through tone, facial expression, or behavior, adjusting environments accordingly for improved well-being.
9. Tips for Building a Smart Home
If you’re considering transforming your home into a smart one, here are a few essential tips:
- Start Small: Begin with one or two devices like smart lighting or a thermostat, then expand gradually.
- Choose a Hub: Use a central hub such as Alexa, Google Home, or Apple HomeKit to control all devices.
- Prioritize Security: Change default passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and update firmware regularly.
- Check Compatibility: Ensure devices are compatible with your ecosystem to avoid integration issues.
- Plan Network Capacity: A strong Wi-Fi network is essential for seamless IoT communication.
- Set Automation Rules: Create customized routines that fit your lifestyle, such as morning lighting or bedtime schedules.
10. Balancing Innovation with Privacy and Ethics
As technology becomes more embedded in our lives, ethical questions surrounding data usage, consent, and digital autonomy grow increasingly important. Companies developing IoT devices must prioritize transparency and data protection. Governments, too, need to establish stronger regulations to ensure responsible innovation.
For users, understanding how data is collected and used is crucial. Informed choices, combined with proper security practices, can strike a balance between enjoying convenience and preserving privacy.
Conclusion
The World of Smart Homes and IoT Devices represents a monumental leap forward in human innovation. It’s not just about automating lights or thermostats—it’s about creating intelligent ecosystems that enhance comfort, safety, and sustainability. With IoT technology advancing rapidly, our homes are evolving into smart environments that learn, adapt, and grow with us.