Regulatory Push and Corporate Sustainability Targets Accelerate Market Growth
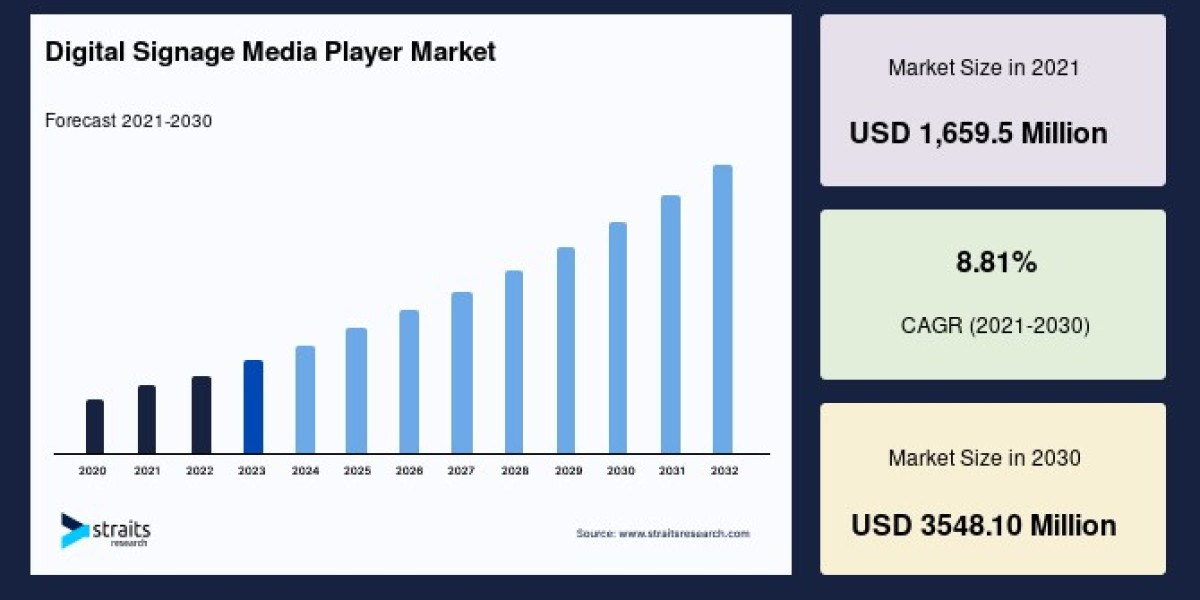
According to the latest report by Market Intelo, the global Emission Trading System market was valued at USD 67.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 140.6 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 9.8% during the forecast period (2024–2032). The market’s growth is primarily driven by stringent environmental regulations, the rapid adoption of carbon pricing mechanisms, and increased participation from corporate entities aiming to meet net-zero emission goals.
As nations worldwide intensify efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, emission trading systems (ETS) have emerged as a cornerstone of market-based climate policies. These systems enable organizations to buy and sell emission allowances, effectively creating a financial incentive for reducing carbon output. The increasing global focus on carbon neutrality and climate risk mitigation is accelerating ETS implementation across various industries.
Get Sample Report of Emission Trading System Market @ https://marketintelo.com/request-sample/3447
Market Overview
Emission trading systems function as cap-and-trade mechanisms that set limits on total emissions and allow market participants to trade allowances based on their emission levels. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide have embraced ETS frameworks to achieve emission reduction targets in a cost-effective and scalable manner.
Currently, over 30 countries operate national or regional ETS programs, including the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS), China’s National ETS, and California’s Cap-and-Trade Program. These initiatives collectively cover nearly 25% of global greenhouse gas emissions, highlighting the growing significance of emission trading in global climate governance.
Get Sample Report of Emission Trading System Market @ https://marketintelo.com/request-sample/3447
Market Dynamics
The growth of the global Emission Trading System market is underpinned by multiple factors. One of the most influential drivers is the growing emphasis on global decarbonization initiatives. Governments are introducing strict emission reduction regulations and setting ambitious carbon neutrality targets, encouraging industries to adopt market-based carbon management systems. Additionally, corporations are increasingly engaging in emission trading to meet environmental, social, and governance (ESG) benchmarks and reduce their carbon liabilities.
The expansion of regional cap-and-trade programs in Asia-Pacific and North America is further broadening market participation. Technological advancements, particularly in blockchain and artificial intelligence, are transforming emission tracking, verification, and trading operations by increasing transparency and accuracy. However, market growth is not without challenges. Fluctuations in carbon credit prices, inconsistent regulatory frameworks between regions, and limited engagement from developing economies pose obstacles to market stability and scalability. Concerns about carbon leakage and inequitable allocation of allowances also continue to surface.
Despite these challenges, the market presents significant opportunities. The rise of voluntary carbon markets and the integration of digital carbon registries are opening new avenues for investment. Emerging economies are exploring ETS adoption as a sustainable development strategy that aligns industrial growth with international carbon reduction commitments.
Read Full Research Study: https://marketintelo.com/report/emission-trading-system-market
Market Segmentation
The Emission Trading System market can be analyzed by type, application, and component. Based on type, the market is divided into cap-and-trade systems and baseline-and-credit systems. Among these, the cap-and-trade system dominates due to its extensive implementation across governments and proven ability to reduce emissions effectively.
By application, the market is segmented into power generation, industrial manufacturing, aviation, transportation, and other sectors. The power generation segment currently accounts for the largest market share, as electricity production remains one of the world’s primary sources of carbon emissions. Meanwhile, the aviation and transportation segments are expected to grow rapidly as international emission standards tighten and carbon offset programs gain traction among airlines and logistics companies.
In terms of components, the market is categorized into registry platforms, trading platforms, and verification services. Trading platforms are expected to register strong growth during the forecast period, driven by the proliferation of digital exchanges and blockchain-based carbon marketplaces that facilitate secure, efficient, and transparent transactions.
Regional Insights
Europe continues to lead the global Emission Trading System market, supported by the success of the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS). This program has significantly reduced carbon emissions across power and industrial sectors while establishing a robust carbon pricing mechanism. Strong regulatory frameworks, ambitious sustainability goals, and rising carbon credit values continue to reinforce the region’s leadership in this market.
North America follows closely, with the United States and Canada demonstrating robust participation through regional initiatives like the California Cap-and-Trade Program and the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI). The region’s focus on achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 and its growing investment in clean energy infrastructure are sustaining market expansion.
The Asia-Pacific region is projected to record the fastest growth in the coming years. China’s national ETS—the largest in the world—has become a benchmark for other emerging economies in the region. South Korea, Japan, and New Zealand are also advancing their carbon trading frameworks to meet the objectives of the Paris Agreement. Rapid industrialization, government-backed sustainability policies, and cross-border cooperation are boosting regional market growth.
Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are also showing increasing interest in emission trading systems. Brazil, Chile, and South Africa are among the early adopters in these regions, and their programs are expected to grow as they integrate ETS models with renewable energy initiatives and sustainable land-use policies.
Competitive Landscape
The Emission Trading System market is moderately consolidated, with a mix of global and regional players driving competition through technological innovation, strategic alliances, and digital transformation. Key companies operating in this space include Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), European Energy Exchange (EEX), NASDAQ OMX Commodities, Shanghai Environment and Energy Exchange, Chicago Climate Exchange (CCX), BlueNext SA, Korea Exchange (KRX), Powernext, Climate Impact X (CIX), and AirCarbon Exchange (ACX).
These organizations are investing heavily in digital trading infrastructure, automated verification technologies, and blockchain-based carbon credit systems to improve efficiency, enhance transparency, and attract new participants. Their strategies are focused on expanding cross-border trading opportunities and strengthening market credibility.
Technological Advancements Shaping the Market
Innovation plays a central role in enhancing the operational efficiency of emission trading systems. Blockchain technology ensures transparent and tamper-proof trading transactions, while artificial intelligence facilitates carbon pricing forecasts, compliance monitoring, and risk assessment. The integration of IoT-enabled emission sensors and satellite monitoring is further improving real-time emission tracking and verification, which is critical for regulatory compliance and corporate reporting accuracy.
These technological advancements not only enhance efficiency but also build investor and public confidence in ETS mechanisms, driving further adoption across sectors.
Future Outlook
The global Emission Trading System market is poised for continued growth as more countries implement carbon pricing schemes to achieve climate goals. By 2032, the market is expected to evolve into a fully interconnected global carbon trading ecosystem, merging compliance and voluntary systems for greater liquidity and transparency.
Corporate participation, supported by digital trading solutions and government incentives, will continue to fuel this expansion. Investments in data infrastructure, regulatory harmonization, and cross-border trading mechanisms will be key to realizing the full potential of ETS frameworks in mitigating climate change.
Conclusion
The Emission Trading System market stands at the forefront of the global transition toward a low-carbon economy. It represents a market-driven solution for reducing greenhouse gas emissions while encouraging innovation and economic efficiency. With regulatory momentum, corporate commitment, and technological progress accelerating simultaneously, the ETS market is set to play a defining role in achieving carbon neutrality by 2032.
Organizations that invest early in emission trading capabilities and digital carbon management infrastructure will be better positioned to navigate future sustainability challenges and capitalize on the growing global carbon market.
Related Report