Ultra-thin Glass Market continues to expand as technology companies increasingly rely on its exceptional flexibility, strength, and optical clarity. From smartphones and tablets to wearables and foldable screens, ultra-thin glass is becoming the material of choice for modern electronic design. Its combination of light weight and durability allows manufacturers to push design boundaries, creating sleeker, more resilient devices that enhance user experience. As global demand for connected gadgets grows, this specialized material is evolving into a core component of next-generation electronics.
Expanding Use in Smart Devices and Displays
Ultra-thin glass plays a crucial role in today’s display technologies. Its smooth surface and high transparency enable sharper visuals, vibrant colors, and superior touch sensitivity. Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating it into OLED and AMOLED screens for smartphones and televisions, where flexibility and precision are vital.
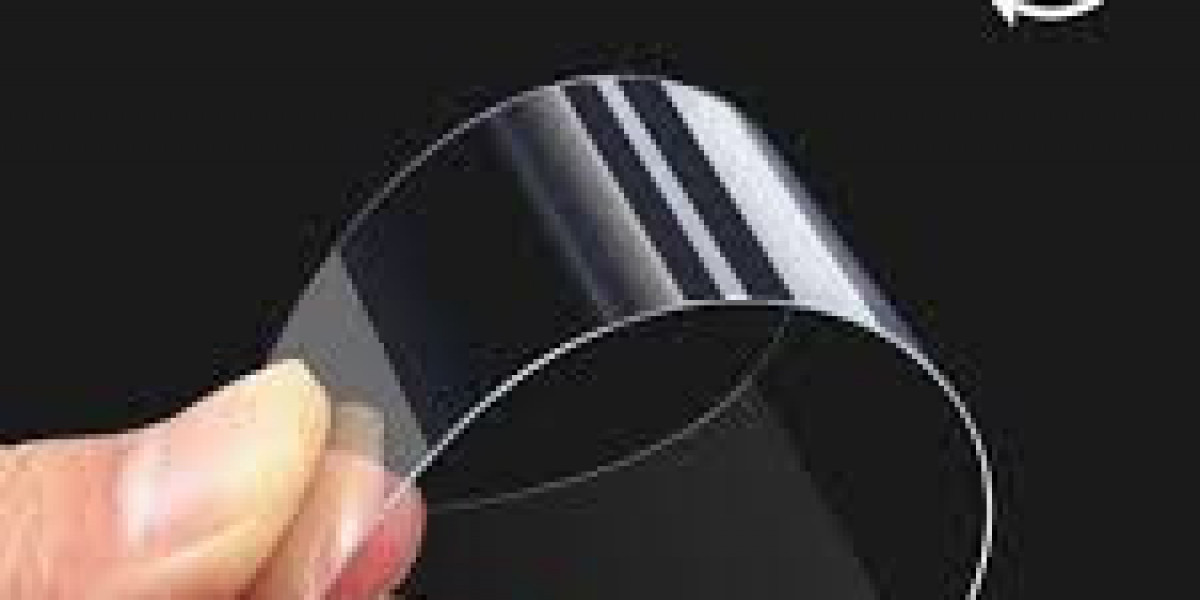
The material’s unique ability to bend without breaking has revolutionized foldable and rollable display designs. This innovation allows device makers to deliver larger, more versatile screens while maintaining compact portability. As wearable technology, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) devices gain traction, ultra-thin glass provides the necessary combination of visual clarity, flexibility, and durability required for immersive experiences.
Durability and Design Flexibility
Modern consumers demand devices that are both durable and aesthetically appealing. Ultra-thin glass delivers these attributes through advanced manufacturing techniques that enhance its strength despite minimal thickness. Chemically strengthened glass variants resist scratches, cracks, and impacts, ensuring long-lasting performance under everyday use.
The ability to produce glass at thicknesses below 0.5 millimeters while maintaining mechanical stability allows product designers to achieve ultra-slim profiles without sacrificing quality. This flexibility encourages creative engineering, enabling the production of lightweight devices with minimal bezels and seamless curved edges.
Role in Foldable and Wearable Electronics
Foldable smartphones and tablets have emerged as a key trend in consumer electronics, with ultra-thin glass at the center of this transformation. The material’s bendability allows repeated folding while retaining touch responsiveness and structural integrity. Unlike plastic alternatives, ultra-thin glass offers superior hardness and resistance to deformation, maintaining visual clarity even after prolonged use.
In wearable devices such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, ultra-thin glass provides both protection and style. It offers a scratch-resistant surface that supports high-resolution displays while ensuring comfort and durability. Its capacity to be shaped into complex forms also enables seamless integration into curved or flexible designs.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Benefits
Sustainability has become an essential factor in consumer electronics manufacturing, and ultra-thin glass supports eco-friendly design initiatives. Its lightweight composition reduces overall material consumption, while recyclability contributes to circular economy objectives.
Energy-efficient production methods, including low-temperature coating and optimized cutting processes, further minimize environmental impact. Manufacturers are also exploring methods to integrate ultra-thin glass into solar-enabled smart devices, helping improve energy efficiency and battery life. As technology moves toward greener solutions, this material offers both performance and environmental compatibility.
Technological Innovations in Manufacturing
Continuous innovation in production technologies has enabled ultra-thin glass to meet the rigorous requirements of the smart device market. Precision manufacturing methods such as float processes, chemical tempering, and ion exchange ensure exceptional uniformity and strength.
Emerging coating technologies enhance anti-reflective properties, fingerprint resistance, and light transmission, improving both functionality and aesthetics. These advancements ensure that ultra-thin glass remains compatible with touch sensors and high-resolution displays used in premium electronic devices.
Furthermore, digital manufacturing techniques and automation systems are improving production efficiency, reducing defects, and enhancing scalability. As global demand rises, manufacturers are investing in larger and more sophisticated production lines capable of delivering high volumes with consistent quality.
Integration in Smart Home and IoT Devices
Beyond mobile and wearable technology, ultra-thin glass is gaining prominence in smart home and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It is increasingly used in smart mirrors, connected appliances, and touch-enabled control panels that require durable and visually appealing interfaces.
Its ability to transmit signals without interference makes it ideal for devices equipped with sensors and connectivity modules. The integration of ultra-thin glass into home automation systems enhances durability while maintaining sleek and modern aesthetics, aligning with consumer preferences for minimalist design.
Market Expansion Across Global Regions
The ultra-thin glass market is experiencing strong global growth, driven by expanding electronics manufacturing hubs in Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America. Countries like China, South Korea, and Japan lead in production and innovation due to their established display technology industries. Meanwhile, demand in North America and Europe continues to rise, fueled by increasing adoption of advanced consumer electronics and smart home systems.
Strategic collaborations between glass manufacturers and technology firms are fostering rapid development of next-generation materials. These partnerships are accelerating innovation cycles and ensuring that ultra-thin glass maintains its competitive edge in design flexibility, performance, and sustainability.
Challenges and Future Opportunities
While the ultra-thin glass market is flourishing, it also faces challenges related to manufacturing complexity and cost management. Producing defect-free glass at sub-millimeter thickness requires precision machinery and stringent quality control. However, ongoing advancements in automation and digital process optimization are gradually reducing production costs, making ultra-thin glass more accessible for mass-market applications.
Future opportunities lie in the development of smart coatings, improved folding durability, and hybrid materials that combine glass with polymers for added resilience. As demand for flexible electronics and connected devices continues to grow, these innovations will further expand the market’s potential.
Outlook for the Ultra-thin Glass Market in Smart Devices
The future of the ultra-thin glass market is closely tied to the evolution of consumer electronics. As new generations of foldable, wearable, and energy-efficient devices emerge, ultra-thin glass will remain at the forefront of innovation. Its unmatched combination of strength, lightness, and design adaptability ensures it will continue shaping the technological landscape.
With continuous advancements in manufacturing, sustainability, and application diversity, ultra-thin glass is set to become the defining material of next-generation smart consumer products. Its integration into global production ecosystems reflects not only technological progress but also the broader shift toward smarter, greener, and more efficient materials for modern living.