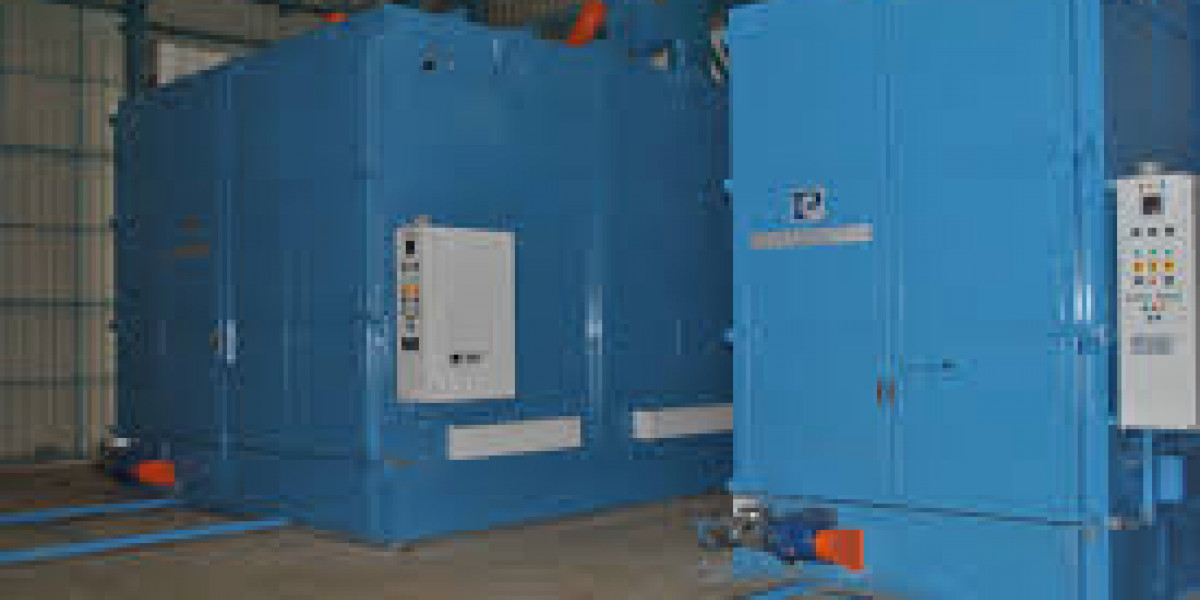
Burn-off Oven Market witnessing investments in R&D for enhanced durability and process optimization is growing as industries demand advanced thermal cleaning technologies that balance performance, safety, and sustainability. Burn-off ovens, which use controlled heat to remove coatings, paints, and polymers, are critical tools in automotive, aerospace, electrical, and manufacturing sectors. With rising industrial automation and environmental compliance requirements, manufacturers are investing in innovation to improve oven design, material strength, and operational precision.
Emphasis on Research and Material Innovation
Ongoing research focuses on enhancing the structural durability of burn-off ovens to withstand continuous high-temperature operations. Developers are incorporating corrosion-resistant alloys, advanced insulation materials, and reinforced chamber designs to ensure longer service life. These innovations reduce maintenance needs and improve thermal consistency. Such advancements not only enhance reliability but also make the ovens more cost-effective and efficient in industrial environments with heavy workloads.
Process Optimization for Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency has become a central goal of R&D in this market. Manufacturers are designing systems that utilize heat recovery units, improved airflow management, and digital temperature control to minimize energy waste. By optimizing combustion processes and introducing low-emission burners, burn-off ovens are now capable of delivering cleaner performance with reduced fuel consumption. These developments support industries aiming to lower operational costs while meeting sustainability objectives.
Automation and Smart Control Integration
Modern industrial operations require precise process management. To meet these demands, manufacturers are integrating automation technologies and smart control systems into burn-off ovens. Real-time monitoring enables accurate temperature regulation, safety control, and cycle optimization. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and data-driven interfaces allow users to adjust parameters according to material type and coating thickness, enhancing flexibility and consistency. These automated systems also improve workplace safety and reduce operator intervention.
Focus on Environmental Compliance
Environmental regulations have pushed industries to adopt equipment that minimizes harmful emissions and waste. R&D efforts now emphasize emission control systems such as secondary afterburners and catalytic oxidation units, ensuring cleaner exhaust. This approach aligns with global goals for industrial decarbonization. Furthermore, manufacturers are developing models capable of operating efficiently on alternative fuels or renewable energy sources, supporting the transition toward greener manufacturing.
Expanding Industrial Applications
Advancements in durability and process optimization have expanded the usability of burn-off ovens across diverse sectors. Aerospace industries rely on them for cleaning high-value tools and components, while the automotive and electrical industries use them for refurbishing coated parts. Metal fabrication units benefit from consistent cleaning of jigs, hooks, and fixtures. The improved performance characteristics developed through R&D make these ovens suitable for demanding industrial environments.
Regional Growth Driven by Technological Upgrades
Industrial modernization in regions such as Asia-Pacific and Europe is contributing significantly to market expansion. Manufacturers in these areas are upgrading to next-generation burn-off ovens equipped with advanced heat recovery and automation features. The rising demand from small and medium-sized enterprises for compact, durable, and cost-efficient models is further fueling innovation. Regional collaborations between research institutes and manufacturers are also accelerating the pace of product development.
Future Outlook for R&D in Burn-off Ovens
The future of the burn-off oven market lies in intelligent systems capable of self-diagnosis, predictive maintenance, and energy optimization. Research is increasingly directed toward developing modular oven designs that can be easily customized for specific industrial requirements. In addition, integration with Industry 4.0 technologies will enable digital connectivity, allowing for greater control and operational insight. Continuous investment in R&D will ensure that burn-off ovens remain indispensable in sustainable industrial cleaning.
Conclusion
Investments in research and development are reshaping the burn-off oven market by introducing more durable, energy-efficient, and environmentally compliant solutions. Enhanced materials, optimized processes, and smart automation are enabling industries to achieve higher productivity with lower costs and minimal ecological impact. As global industries move toward sustainable modernization, these innovations will continue to strengthen the role of burn-off ovens in future-ready manufacturing systems.