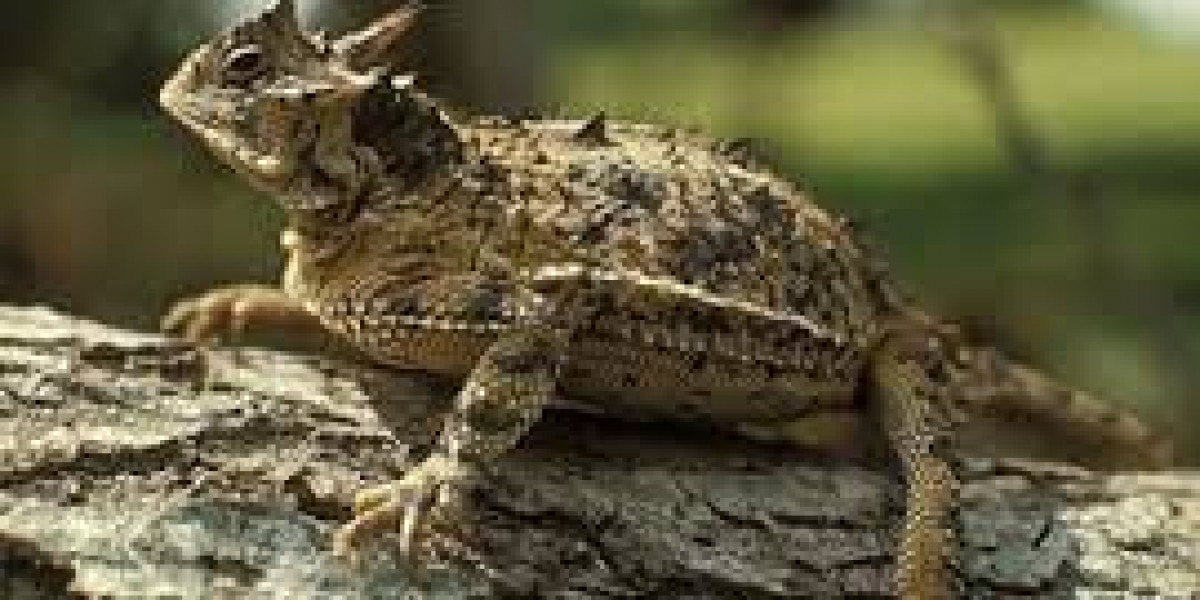
Horned lizards are fascinating desert reptiles, famous for their spiky bodies and odd defense strategies like shooting blood from their eyes. But if you’ve ever seen one in the wild, you might wonder: what exactly do horned lizards eat? Their diet is surprisingly specialized and plays a crucial role in their survival. Understanding what these little “monsters” consume can also explain why they are so sensitive to environmental changes.
Horned lizards primarily eat ants, especially harvester ants, in the wild. They may also consume other insects such as beetles, spiders, and grasshoppers, but ants make up the bulk of their diet. Their feeding habits are highly specialized, making them sensitive to changes in habitat or prey availability.
The Ant-Based Diet
Horned lizards are known for their preference for ants, particularly harvester ants, which provide both nutrition and energy. These ants are abundant in desert and grassland habitats, and horned lizards have evolved to hunt them efficiently. Their sticky tongues and slow, patient hunting style allow them to consume large quantities without harming themselves. In fact, some horned lizards can eat hundreds of ants in a single day. This ant-focused diet is so important that it directly influences where horned lizards can live and thrive. Without access to native ant colonies, horned lizards struggle to survive, which is why invasive species like fire ants are such a threat.
Other Insects in Their Diet
While ants are their main food source, horned lizards are opportunistic and will eat other insects if available. Beetles, grasshoppers, crickets, and spiders may occasionally appear on their menu, providing protein and nutrients that supplement their ant-heavy diet. However, these insects do not replace the nutritional value of harvester ants. Horned lizards have digestive systems specifically adapted to process the formic acid in ants, which makes other prey less critical for survival.
Hunting and Feeding Behavior
Horned lizards are patient hunters. They often remain motionless on the ground, blending perfectly with sandy or rocky terrain to avoid predators while waiting for ants to pass by. When a trail of ants comes close, the lizard flicks its tongue to capture them efficiently. Their feeding strategy is energy-efficient, which is crucial in hot desert environments where movement and water loss must be minimized. This specialized hunting technique also explains why horned lizards are rarely seen actively roaming in search of food. They rely on strategic ambush tactics rather than chasing prey.
Why Diet Matters for Survival
The reliance on ants makes horned lizards vulnerable to changes in their environment. Pesticides, habitat destruction, and invasive ant species reduce the availability of harvester ants, directly threatening lizard populations. This dietary specialization also explains why horned lizards make poor pets—most captive diets cannot replicate the nutrients found in native ants. Even when offered alternative insects like mealworms or crickets, horned lizards often fail to thrive. In the wild, their survival is intricately tied to the health of ant populations and the quality of their desert habitat.
Ecological Importance of Their Diet
By feeding primarily on ants, horned lizards play an important ecological role. They help regulate ant populations, maintaining balance in desert ecosystems. This predator-prey relationship is critical for the overall health of the habitat. Additionally, horned lizards themselves serve as prey for larger animals, meaning their specialized diet indirectly supports the wider food chain. Understanding what horned lizards eat highlights not only their unique adaptations but also their role as a keystone species in desert ecosystems.
Conclusion
Horned lizards are fascinating creatures whose survival depends heavily on a specialized diet. Ants, particularly harvester ants, form the backbone of their nutrition, while other insects provide occasional supplementation. Their unique feeding behaviors, reliance on native ant colonies, and ecological importance make them highly sensitive to environmental changes. Protecting horned lizard habitats ensures that these remarkable little reptiles can continue to thrive in the wild. Observing their diet offers insight into the delicate balance of desert ecosystems and the evolutionary adaptations that make horned lizards true masters of survival.
FAQs
What is the primary food of horned lizards?
Harvester ants make up the majority of a horned lizard’s diet in the wild.
Do horned lizards eat other insects?
Yes, they may eat beetles, spiders, grasshoppers, and crickets as supplemental food.
Why can’t horned lizards eat just any insects in captivity?
Their digestive systems are adapted to process ants’ formic acid, so alternative insects may not provide proper nutrition.
How do horned lizards hunt ants?
They ambush ants by remaining motionless and flicking their sticky tongues to capture them efficiently.
How does their diet affect their survival?
Availability of native ants is critical; habitat loss, pesticides, and invasive species can drastically reduce food sources and threaten populations.