Tempered glass has become an essential material in today’s construction and design industries. Valued for its exceptional strength and safety features, tempered glass is widely used in residential, commercial, and automotive applications. Its ability to resist impact, tolerate heat, and reduce injury risks makes it one of the most reliable glass solutions available.
Understanding Tempered Glass
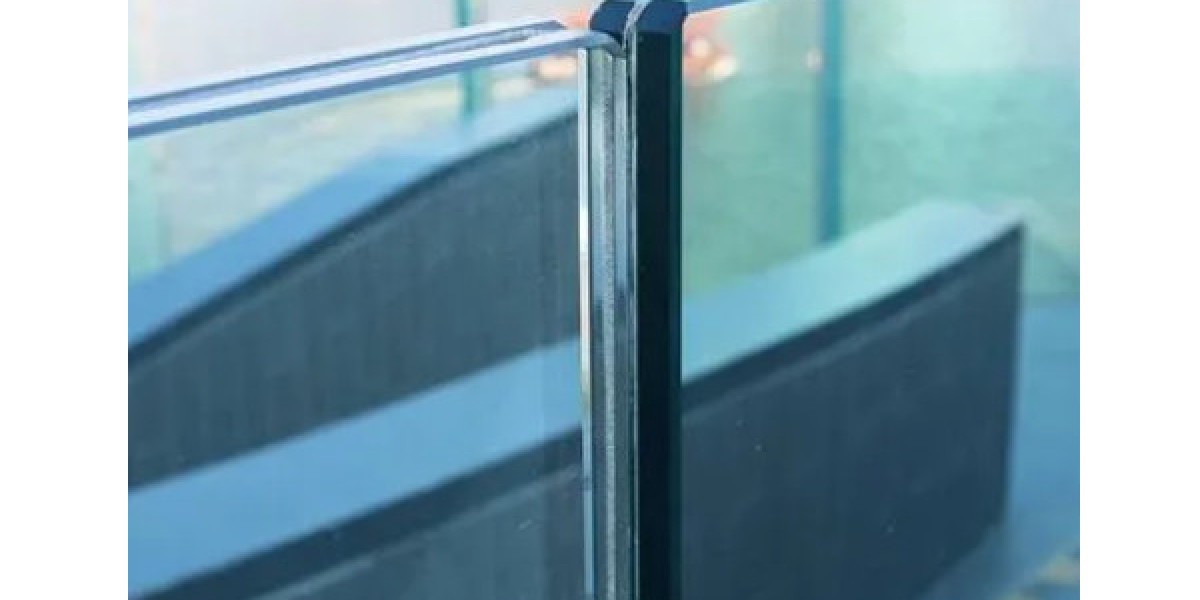
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass that undergoes a specialized heat treatment process to enhance its durability. Unlike ordinary glass, tempered glass is engineered to handle high stress and sudden temperature changes. When broken, it crumbles into small, rounded fragments rather than sharp shards, minimizing the risk of serious injury.
The Tempering Process Explained
The production of tempered glass involves a precise and controlled method:
High-Temperature Heating
Glass sheets are heated to over 600°C, allowing them to reach a softened state.
Rapid Cooling
Cold air is applied to the surface, cooling the outer layers quickly while the inner layers cool slowly.
Internal Strength Formation
This process creates compression on the surface and tension inside, making the glass much stronger than standard glass.
Once tempered, the glass cannot be cut, drilled, or reshaped, as any alteration may cause it to shatter.
Advantages of Tempered Glass
Improved Safety
Tempered glass is designed to break safely, reducing the chance of cuts or injuries.
High Durability
It is up to five times stronger than annealed glass, making it ideal for demanding environments.
Thermal Resistance
Tempered glass can endure extreme temperature changes without cracking.
Low Maintenance
The smooth surface resists scratches, moisture, and stains, making it easy to clean.
Modern Appearance
Its sleek and polished finish enhances the visual appeal of any space.
Applications of Tempered Glass
Residential Use
Shower doors and bathtub enclosures
Windows and sliding glass doors
Glass shelves and tabletops
Commercial Use
Office partitions and conference rooms
Storefronts and display windows
Glass railings and staircases
Automotive Industry
Side and rear vehicle windows
Public Spaces
Bus shelters and safety barriers
Elevator panels and escalator sides
Tempered Glass vs Regular Glass
| Feature | Tempered Glass | Regular Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Very High | Low |
| Safety | Shatters safely | Sharp shards |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
| Durability | Long-lasting | Easily damaged |
Is Tempered Glass Worth the Investment?
Although tempered glass may cost slightly more than standard glass, its safety, durability, and long lifespan make it a cost-effective choice in the long run. Many building codes now require tempered glass in high-risk areas, making it both a practical and regulatory-compliant solution.
Conclusion
Tempered glass stands out as a premium glazing option that combines strength, safety, and style. From modern homes to commercial buildings, its versatility and performance make it the preferred choice for architects and homeowners alike. Choosing tempered glass means investing in long-term protection, visual elegance, and peace of mind.