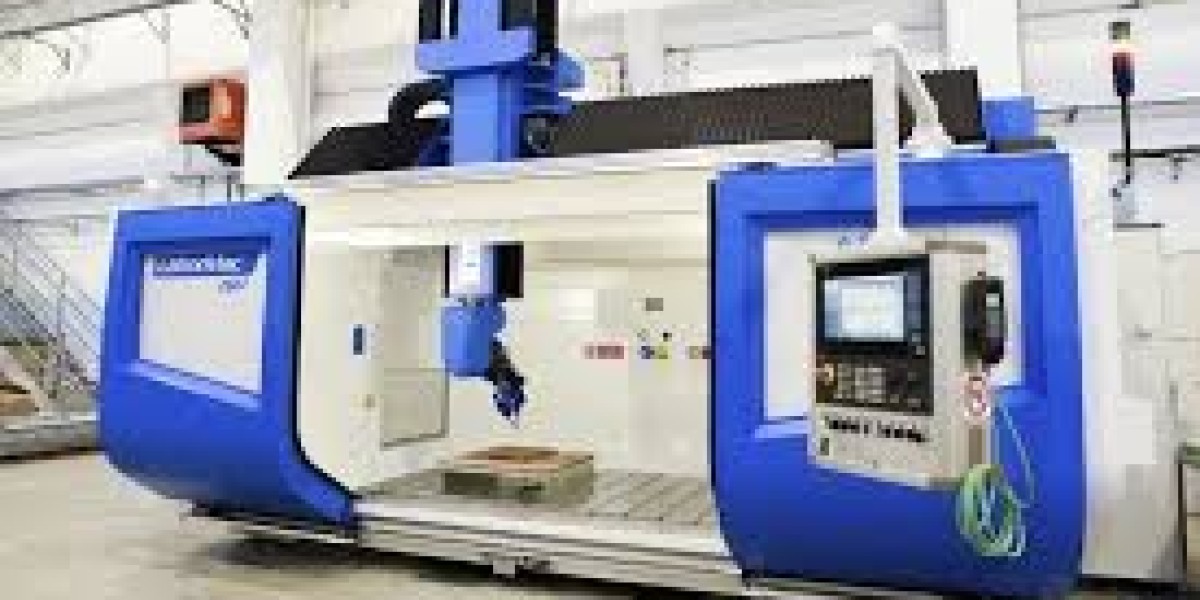
In modern manufacturing, speed-to-market is critical. Whether launching a new medical device, refining an automotive component, or iterating on a consumer gadget, the ability to produce functional prototypes rapidly can define commercial success or failure.
This is where rapid CNC prototyping plays a transformative role.
By eliminating tooling delays and enabling fast, accurate machining of real materials, CNC prototyping dramatically accelerates product development cycles. Engineers and designers can now test, validate, and iterate components in days—not weeks—without compromising on performance or quality.
What Is Rapid CNC Prototyping?
Rapid CNC prototyping is the process of using computer numerical control (CNC) machines to quickly manufacture functional prototype parts from solid materials. Unlike traditional production methods that require molds or casting tools, CNC machining is a tool-less, subtractive process that uses digital files (CAD/CAM) to remove material from a block.
This method supports:
Low-volume production without tooling investment
Tight tolerances, often as low as ±0.01 mm
Wide material compatibility including metals, plastics, and composites
Fast lead times, with parts ready in 1–5 days
Because CNC-machined prototypes are made from end-use materials, they offer a realistic evaluation of mechanical, thermal, and structural performance—making them ideal for both form and function testing.
Why Speed Matters in Product Development
Delays in prototype production have a domino effect on the entire product lifecycle. When early designs take weeks to materialize into physical parts, engineering teams lose momentum, and time-to-market increases.
Rapid CNC prototyping mitigates this risk by:
Allowing early physical validation of digital models
Supporting fast iteration loops across multiple design revisions
Providing testable parts that mimic final performance
Enabling parallel development of prototypes and production strategies
In a competitive market, shaving even a few weeks off the R&D cycle can offer significant strategic and financial advantages.
How Rapid CNC Prototyping Works
The CNC prototyping process typically involves the following steps:
CAD Design: Engineers design the part in a CAD software (e.g., SolidWorks, Fusion 360).
CAM Programming: Toolpaths are generated to guide cutting tools across the part geometry.
Machine Setup: A machinist sets up the raw material, tooling, and workholding.
Machining: The part is cut from the block with precision milling or turning operations.
Post-Processing: Deburring, finishing, or inspection is performed as needed.
With an optimized workflow and digital quoting, some CNC shops deliver parts in under 48 hours—ideal for early-stage validation, design-for-manufacturing (DFM) testing, and functional use cases.
Applications of CNC Prototyping in Key Industries
Rapid CNC prototyping is used in nearly every product-based sector. Here’s how it benefits specific industries:
✅ Aerospace and Defense
Machined brackets, housings, and mechanical test articles
Functional testing of aluminum and titanium parts
Validation of load-bearing components before production
✅ Medical Devices
PEEK and titanium surgical tools or implant prototypes
Small-batch trials for regulatory testing
Complex geometries verified via multi-axis CNC
✅ Automotive and Mobility
Engine parts, control arms, suspension prototypes
Fit and durability testing in high-temperature environments
Short-run production for motorsports or custom vehicles
✅ Consumer Electronics
Enclosures, mounts, and interface mechanisms
Transparent prototypes with polished acrylic or polycarbonate
Pilot production runs for product pitches or crowdfunding
✅ Robotics and Automation
Precision components for actuators, gears, and sensor mounts
Integrated electromechanical prototypes
Lightweight structures optimized for movement and stress
CNC vs. 3D Printing for Prototyping
While both CNC and 3D printing are rapid prototyping methods, their applications differ:
| Attribute | CNC Prototyping | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Material Range | Metals and high-performance plastics | Limited metals, mostly polymers |
| Tolerances | ±0.01 mm or better | ±0.1 mm (typical) |
| Strength | Functional load-bearing parts | Often weak in Z-direction |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, high-end finish | Layered, needs post-processing |
| Machining Complexity | Complex but tool-access dependent | Freeform geometry, no tool access needed |
| Setup Time | Minimal, if material is in stock | Almost none |
Verdict:
Use CNC when mechanical strength, heat resistance, and dimensional precision are required. Use 3D printing for early visual models or complex internal geometries.
Materials Used in CNC Prototyping
CNC machining supports a broad range of prototyping materials, enabling both testing and production-alike results.
Common CNC Materials:
| Category | Examples | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Brass | Functional and structural parts |
| Plastics | ABS, PEEK, Nylon, Polycarbonate | Lightweight, insulative, or medical-grade parts |
| Others | Acrylic, Copper, Titanium | Aesthetic, conductive, or high-strength uses |
Selecting the right material ensures compatibility with end-use conditions such as impact, heat, or biocompatibility.
Benefits of Rapid CNC Prototyping
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Fast Turnaround | Parts delivered in 1–5 business days |
| Real Materials | Prototypes made from the same materials as final parts |
| Tight Tolerances | Enables validation of assembly fit, function, and durability |
| Repeatability | Ideal for multiple iterations with controlled quality |
| Scalable to Production | Same setup can transition to low-volume production |
By accelerating feedback loops and reducing dependency on molds or tooling, rapid CNC prototyping keeps projects on time and under budget.
From Prototype to Production
One of the biggest advantages of CNC is that once a prototype is finalized, the same CAD/CAM files can be reused for small-batch or even full-scale production runs.
This ensures:
No design transfer delays
Fewer revalidations
Consistent tolerances and machining strategies
Some CNC shops also provide CNC prototyping machining services that include post-processing, surface finishing, and documentation—supporting a complete product development pipeline from concept to market.
Summary: Why Rapid CNC Prototyping Matters
| Key Advantage | Result for Development Teams |
|---|---|
| Fast lead time | Rapid iteration and fewer project delays |
| Functional prototypes | Real-world testing under actual loads |
| Precision parts | Immediate validation of tolerances |
| Low-volume friendly | Cost-effective for 1–1000 parts |
| Scalable production workflow | Seamless handoff to manufacturing |
Final Thoughts
Rapid CNC prototyping bridges the gap between digital design and functional reality.
By allowing product teams to produce testable, high-precision parts without tooling delays, CNC accelerates every phase of the development cycle—from concept to production.
Whether you're validating a titanium aerospace bracket or refining a wearable plastic housing, rapid CNC services give you the speed and control you need to succeed.
Explore reliable CNC prototyping machining services to take your ideas from CAD to real-world testing—faster, smarter, and more efficiently.